
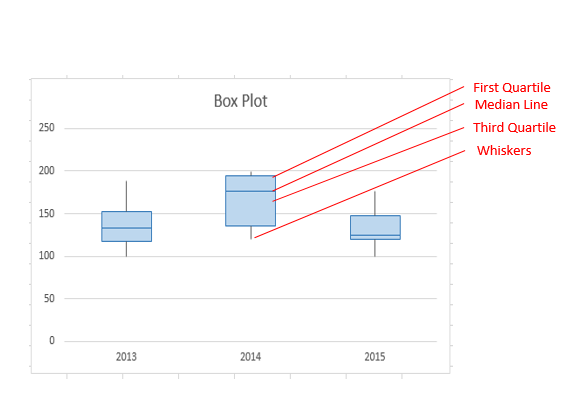
In the box plot template, the whiskers are created by adding Y-error bars to series 1 (Q1) and series 3 (Q3-Q2). Similar change for the lower whisker.Īnother common convention is that instead of extending the whisker to a calculated value of Q 3+1.5(IQR), the whisker is extended to the last data point that is less than or equal to Q 3+1.5(IQR), and similarly with the lower whisker.

The area property is set to none for these two series to create just the outline for the box. These two series, stacked together make up the interquartile range. The first series (bottom column) is Q1 and the border and area properties are set to none so that the column is not visible in the chart. The plot in Excel is created using a stacked column chart with 3 series. If the median is closer to Q1, the distribution is positively skewed. if the median is closer to Q3, the distribution is negatively skewed (or "skewed to the left" meaning the left tail of the distribution is longer). If the distribution is symmetric, the median will be exactly in the middle. The location of the median line relative to the first and third quartiles indicates the amount of skewness or asymmetry in the data. It appears that the older PERCENTILE and QUARTILE functions are the same as PERCENTILE.INC and QUARTILE.INC functions. Note: To exclude the median when calculating the quartiles, you can use the new PERCENTILE.EXC and QUARTILE.EXC functions. The mean is not always displayed in a box plot, but in the new built-in Box and Whisker Chart for Excel 2016+, it is shown as an "x".
The upper edge of the box plot is the third quartile or 75th percentile. The lower edge of the box plot is the first quartile or 25th percentile. The box part of a box and whisker plot represents the central 50% of the data or the Interquartile Range (IQR). An example box and whisker plot from the Box Plot Template showing the IQR, whiskers, and max/min outliers. The appendix includes instructions for creating the box and whisker plot format advocated in this paper, and a sample template is also available for download"-Abstract.Fig 1. A box and whisker plotting convention geared for meteorological applications is described herein, with examples shown using climate data from the WFO Burlington, Vermont forecast area. Lastly, the graphically compact nature of box and whisker plots facilitates side-by-side comparison of multiple datasets, which can otherwise be difficult to interpret using more complete representations, such as the histogram. Common measures of variability, such as standard deviation, may be interpreted based upon an assumption of an underlying standard normal distribution for climate and weather analysis purposes, and might also prove too abstract for non-technical users of climate data. Additionally, the underlying statistics are more resistant toward individual outliers than other methods, such as mean and standard deviation.
#Box and whiskers plot excel 2007 free#
Since box and whisker plots display measures of central tendency and spread free from the assumption of a normal distribution, they provide an effective way of identifying asymmetrical attributes in meteorological datasets. Box and whisker plots offer a pictorial summary of important dataset characteristics including the central tendency, dispersion, asymmetry, and extremes, arrived at through percentile rank analysis and the plotting of maximum and minimum dataset values. "This paper describes the creation and use of box and whisker plots in the statistical analysis of local climate and other hydrometeorological datasets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
